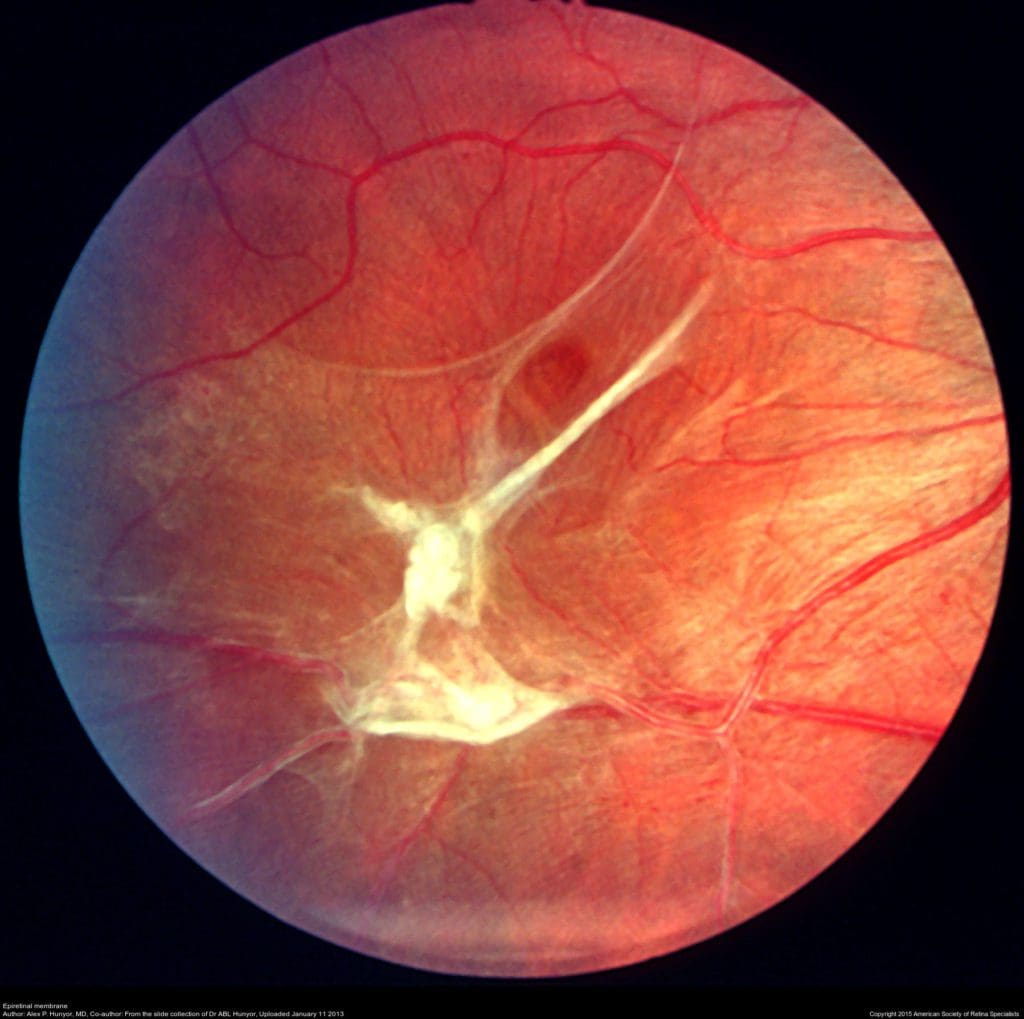
The macula normally lies flat against the back of the eye, like film lining the back of a camera. When wrinkles, creases or bulges form on the macula, this is known as a macular pucker.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NRWY3aIqNss
The macula is the small area at the center of the eye’s retina that allows you to see fine details clearly. The retina is a layer of light-sensing cells lining the back of your eye. As light rays enter your eye, the retina converts the rays into signals, which are sent through the optic nerve to your brain where they are recognized as images. Damage to your macula causes blurred central vision, making it difficult to perform tasks such as reading small print or threading a needle.
What is a macular pucker?
The macula normally lies flat against the back of the eye, like film lining the back of a camera. When wrinkles, creases or bulges form on the macula, this is known as a macular pucker.
What are the symptoms of a macular pucker?
Symptoms of a macular pucker range from mild to severe and may involve one or both eyes and may include:
- Blurred central (detail) vision
- Distorted, or “wavy†vision
- Difficulty reading or performing tasks that require detail vision
- Gray and/or cloudy area in the central vision
- Central blind spot
- Peripheral (side) vision is not affected
What causes macular pucker?
As you age, the vitreous begins to shrink and pull away from the retina. As the vitreous pulls away, scar tissue may develop on the macula. This scar tissue can warp and contract, causing the retina to wrinkle or bulge.
Other eye conditions associated with macular pucker include:
- Torn or detached retina
- Inflammation inside the eye
- Severe trauma to the eye from surgery or injury
- Disorders of the blood vessels in the retina
How is a macular pucker detected?
The doctor detects a macular pucker by examining your retina. He will also obtain optical coherence tomography (OCT) – scans that take special photographs of the eye. These photographs show if an abnormality exists in your retina.
How is a macular pucker treated?
For mild symptoms, no treatment may be necessary. Updating your eyeglass prescription or wearing bifocals may improve vision. Eye drops, medicines or laser surgery do not improve vision.
For more severe symptoms, a surgery called Vitrectomy is recommended. The surgery is usually performed as an outpatient procedure in an operating room. During surgery, Dr. Comaratta uses tiny instruments to remove the wrinkled tissue on the macula. After the tissue is gone, the macula flattens and vision slowly improves, though it sometimes does not return all the way to normal.
What are the risks involved with Vitrectomy surgery?
As with any surgical procedure, complications can occur with Vitrectomy surgery. These complications may include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Retinal detachment
- Recurrence of macular pucker
After Vitrectomy surgery, cataracts (clouding of the eye’s lens) may also develop. Be sure to discuss potential complications with the doctor before your surgery.
